
The ability to accurately read and file your 1040 tax return is something most taxpayers find stressful. With an April 15th deadline looming each year, you’ve probably spent a few hours pouring over your return and the supporting schedules, wondering if you’ve accurately completed the information.
We aim to make this task a little easier by taking you line-by-line through your annual tax return. Let’s get stuck in.
Who should file a tax return?
Most U.S. citizens and permanent residents who work in the United States need to file a tax return if they make more than a certain amount for the year.
Gross income and your tax filing status will dictate whether you need to pay federal income tax and therefore file a tax return.
Gross income
Gross income or taxable income, means all the income you receive in the form of money, goods, property, and services that are not exempt from tax. This also includes income sources outside of the U.S. and from the sale of a home. If your gross income is over the income threshold, you should file a tax return.
Filing status
There are five filing statuses identified by the Internal Revenue Service. Each one has a different income threshold. These thresholds change annually and are available on the IRS website.
Single
Head of household
Married filing jointly
Married filing separate
Qualifying surviving spouse
Self employment taxes are also recorded and filed using tax form 1040, with additional schedules.
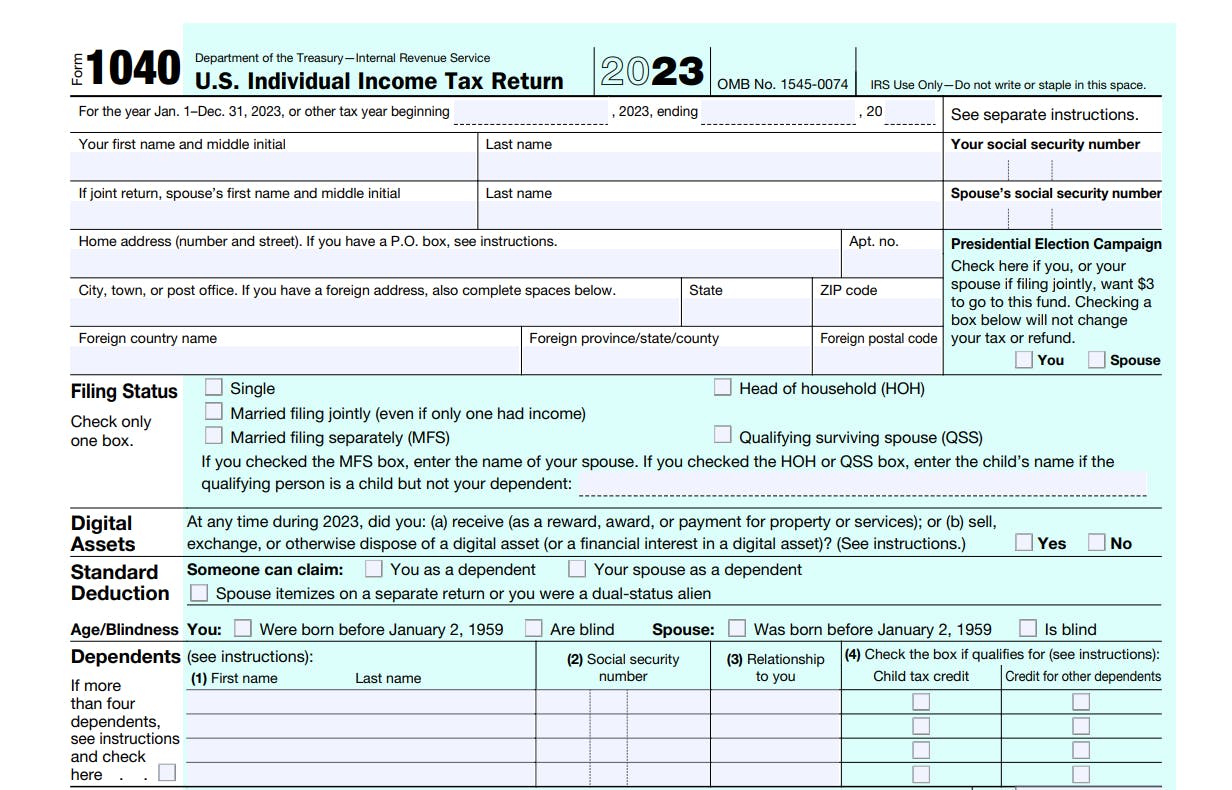
Personal Information Section
irs.gov
Personal information
Complete your personal details, ensuring that the information agrees with government issued identity documents, such as your social security card. Any changes to your surname (due to marriage, divorce, or other reasons) should be reported to the SSA before completing your return.
Social security number
An incorrect or missing SSN can increase your tax, reduce your refund, or delay your refund. Check that both the name and SSN on your Forms 1040 or 1040-SR, W-2, and 1099 agree with your social security card. If they don’t, certain deductions and credits on Form 1040 or 1040-SR may be reduced or disallowed and you may not receive credit for your social security earnings.
Filing status
Check only the filing status that applies to you. If you qualify for more than one filing status, choose the one that would give you the lowest tax.
Digital assets
Digital assets are any digital representations of value that are recorded on a cryptographically secured distributed ledger or any similar technology. For example, digital assets include non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and virtual currencies, such as cryptocurrencies and stablecoins.
Dependants
There are a number of rules that classify a dependant and when you can claim someone as a dependant. IRS Publication 501 provides these guidelines.
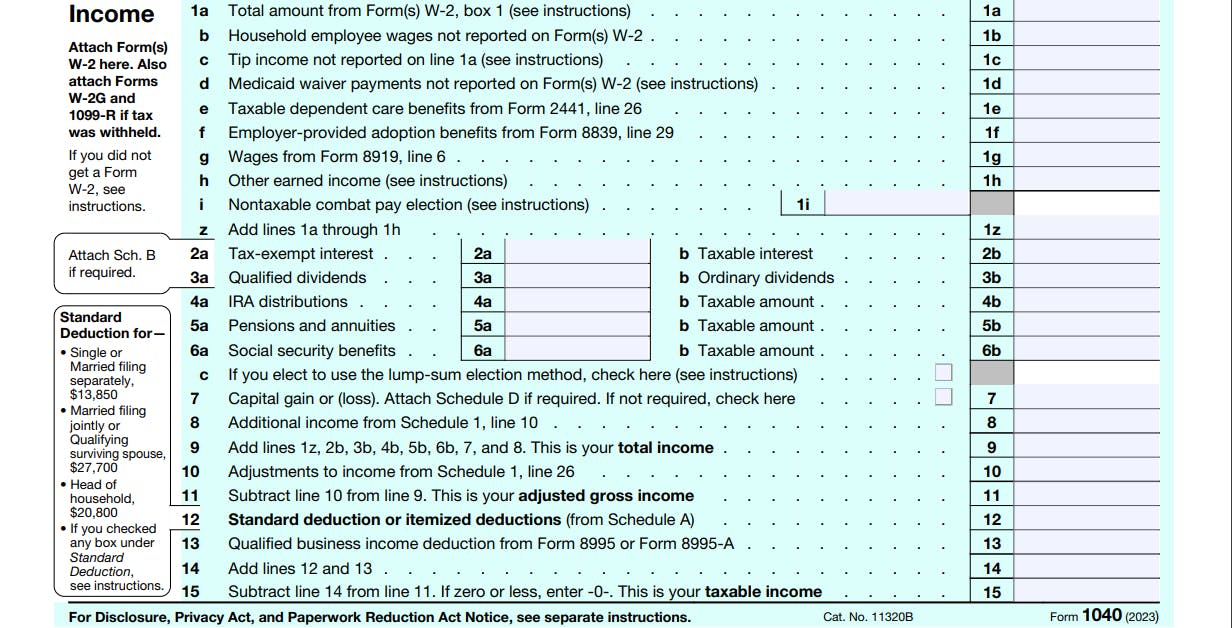
Income Section
irs.gov
Line 1a-h
This is where you enter your income as reported by your W-2 (Wage and Tax Statement), and any additional income as described on the form. These include tips, Medicaid waiver payments, employer provided benefits, wages from Form 8919, line 6, and other income. You will be required to attach your W-2 form.
Make a list of all individual and jointly earned income, and make sure this income is accounted for on the form. Exemptions only apply if they are reported in official IRS communication.
Lines 2ab and 3ab
If you received any tax-exempt interest (including any tax-exempt original issue discount (OID)), such as from municipal bonds, each payer should send you a Form 1099-INT or a Form 1099-OID. Also, include on line 2a any exempt-interest dividends from a mutual fund or other regulated investment company.
Qualified dividends are also included in the ordinary dividend total required to be shown on line 3b. Qualified dividends are eligible for a lower tax rate than other ordinary income. You will also need to fill in Schedule B and attach it to your return.
Lines 4a, 5ab, 6abc
IRA distributions - You should receive a Form 1099-R showing the total amount of any distribution from your IRA before income tax or other deductions were withheld.
Pensions and annuities - You should receive a Form 1099-R showing the total amount of your pension and annuity payments before income tax or other deductions were withheld. Pensions and annuities can be fully taxable or partially taxable.
Social Security benefits - You should receive a Form SSA-1099 showing in box 3 the total social security benefits paid to you. Only check the box on line 6c if you elect to use the lump-sum election method for your benefits.
Line 7
Here you will record capital gains from the sale of a capital asset, such as a stock or bond, you must complete and attach Form 8949 and Schedule D. Two exceptions for filing Form 8949 and Schedule D can be found on the IRS website.
Further reading: How To Avoid Paying Capital Gains Tax on Inherited Property
Line 8
Add any additional income from Schedule 1. This could be income from alimony, business income, gambling, stock options, jury pay, prize money, scholarships, and wages earned while incarcerated. Adjustments from Schedule 1 are added to line 10, and then finally subtracted from line 9, providing your adjusted gross income (line 11).
Line 12
Use Schedule A to work out itemized deductions. These deductions include dental and medical expenses, other taxes paid by you, gifts to charity, interest paid by you, and casualty or theft losses.
Line 13
To figure your Qualified Business Income Deduction, use Form 8995 or Form 8995-A as applicable. The deduction allows eligible taxpayers to deduct up to 20 percent of their QBI, plus 20 percent of qualified real estate investment trust (REIT) dividends and qualified publicly traded partnership (PTP) income. Add lines 12 and 13 (line 14).
Line 15
Subtract line 14 from line 11. This provides your taxable income. Taxable income is the portion of your gross income used to calculate how much tax you owe in a given tax year. It can be described broadly as adjusted gross income (AGI) minus allowable itemized or standard deductions.
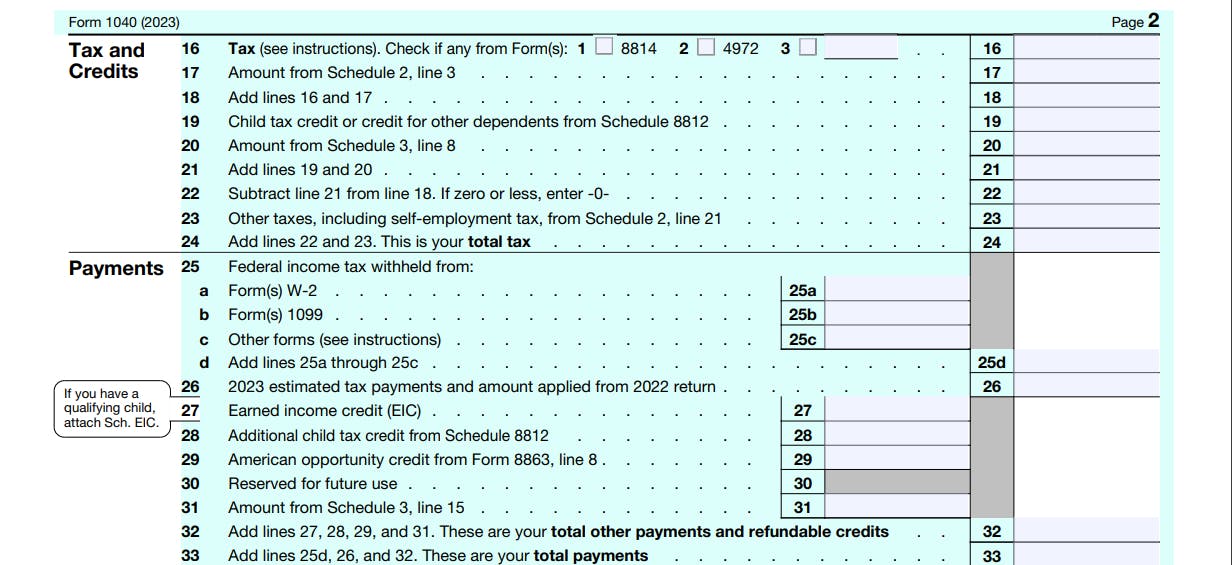
Tax and Credits Section
irs.gov
Lines 16 and 17
Include in the total on the entry space on line 16 all of the following taxes that apply.
Tax on your taxable income.
Tax from Form(s) 8814.
Tax from Form 4972 (relating to lump-sum distributions).
Tax with respect to a section 962 election reduced by the amount of any foreign tax credits claimed on Form 1118.
Recapture of an education credit. You may owe this tax if you claimed an education credit in an earlier year, and either tax-free educational assistance or a refund of qualified expenses was received.
Any tax from Form 8621, line 16e, relating to a section 1291 fund.
Tax from Form 8978, line 14.
Net tax liability deferred under section 965(i).
Triggering event under section 965(i).
Amount from Schedule 2.
Add lines 16 and 17 (line 18), then provide child tax credits from Schedule 8812 (line 19).
Lines 20-24
Enter amounts from Schedule 3, Additional payments, and credits. You can receive credits for child care, education, retirement savings contributions, clean energy, and adoption. These credits can have a significant impact on your final tax bill, and it is suggested you carefully consider Schedule 3 to see if you are eligible for these credits.
Please note: An alternative minimum tax (AMT) places a floor on the percentage of taxes that a filer must pay to the government, no matter how many deductions or credits the filer may claim. Taxpayers have to complete Form 6251 to see whether they might owe AMT.
Don’t miss any deductions or credits that could reduce your tax bill because you simply don’t know about them. Hall Accounting Company provides individual tax planning services for this exact reason. Our professional tax associates are ready to help you reduce your tax liability today.
Payments Section
Line 25a-d
Use your W-2 statement to fill in any tax withheld by your employer. Include on line 25b any federal income tax withheld on your Form(s) 1099-R. Include on line 25 c any federal income tax withheld on your Form(s) W-2G.
Line 26
Enter any estimated federal income tax payments you made for the tax year. Include any overpayment that you applied to the current year’s estimated tax from your previous year’s return or an amended return (Form 1040-X).
If you and your spouse paid joint estimated tax but are now filing separate income tax returns, you can divide the amount paid in any way you choose as long as you both agree. Divorced taxpayers. If you got divorced in the current tax year and you made joint estimated tax payments with your former spouse, enter your former spouse's SSN in the space provided on the front of Form 1040 or 1040-SR.
Line 27
The Earned Income Credit (EIC) is a credit for certain people who work. The credit may give you a refund even if you don’t owe any tax or didn’t have any tax withheld. If you believe you qualify for the EIC, you can confirm this via the ITR website.
Line 28
If you are claiming the additional child tax credit, complete Schedule 8812 and attach it to your Form 1040 or 1040-SR. A caution for taxpayers. If you take this additional credit and it turns out you did not qualify, you will not be allowed to take this credit again for 2 years.
Line 29
If you meet the requirements to claim an education credit enter on line 29 the amount, if any, from Form 8863, line 8.
Lines 30-33
Add the amount from Schedule 3, line 15, and also lines 27,28,29,31 to get your total other payments and refundable credits (line 32). Now add lines 25d, 26, and 32 to get your total payments (line 33).
Tax Refund Section

irs.gov
Line 34
Amount overpaid - If line 34 is under $1, the IRS will send a refund only on written request.
If you owe past-due taxes, state unemployment compensation debts, child support, spousal support, or student loans, all or part of the overpayment on line 34 may be used (offset) to pay the past-due amount.
Line 35a-d
Refund owed to you - Refund information be available within 24 hours after the IRS receives your e-filed return, or 4 weeks after you mail your paper return. For fast refunds provide direct deposit details and the IRS will deposit your refund directly into your cheque or savings account.
Line 36
Is a manual entry of the refund amount you want applied to estimated taxes for the following tax year. This amount will be included in the line 35a calculation, when "Do the Math" is selected.
Amounts You Owe Section
Line 37
Line 37 calculates the amount you owe, subtracting line 33 from line 24. To avoid interest and penalties, pay your taxes in full by the due date of your return (not including extensions) - April 15th for most taxpayers. You don’t have to pay if line 37 is under $1.
There are a number of ways you can pay your taxes. A quick and easy way is to pay online. Other options include your online IRS account, card, digital wallet, or EFW.
If you can't pay the full amount shown on line 37 when you file, you can ask for:
An installment agreement, or
An extension of time to pay.
We know how tough it is when you get an excessive tax bill that you can’t pay right away. Hall Accounting Company’s Tax Associates can help you make arrangements with the IRS to pay your tax in installments. At the same time, they will work with you to keep future payments more manageable.
Line 38
You may owe a penalty if you didn't pay enough estimated tax by any of the due dates. This is true even if you are due a refund.
The law allows the IRS to waive the penalty if you didn’t make the payment due to a natural disaster or if you retired during the tax year and the non-payment was not due to your own negligence.
Third-party designee
If you have opted to take on the services of a tax professional and want them to make contact with the IRS on your behalf, you will need to complete this section, providing names and contact numbers.
Signature
Nearly there now! You can go ahead and sign off your tax return (don’t forget to get your spouse’s signature, if applicable) and submit it to the IRS. Form 1040 or 1040-SR isn't considered a valid return unless you sign it in accordance with the requirements in these instructions.
And you’re done!
Well done if you stuck with our line-by-line explanation of how to read your tax return. We truly hope you’ve benefited from the help. However, if this had the opposite effect on you, and you’ve been left feeling stressed, overwhelmed, and confused by all the schedules, forms, and supporting documentation then ditch the anxiety and get some help from our professional and highly qualified Tax Associates.
They will help you complete your return, but also sit down with you and plan your future tax liability, doing whatever they can to reduce your tax bill and help you put your money into things you care about - instead of the IRS coffers.
